
Language learning is an important asset in today’s globalized world. When one learns another language, he/she can connect with other people and cultures and get good deals and great opportunities (such as jobs with six digit salaries). Learning foreign languages can lead to better decision-making skills, improved memory, an increased attention span, improved multitasking, better cognitive abilities and delayed dementia. Because of these benefits, many parents are interested in having their children learn new languages.
How does one begin with a language and how does one measure one’s abilities in learning and proficiency?
Language Learning Levels
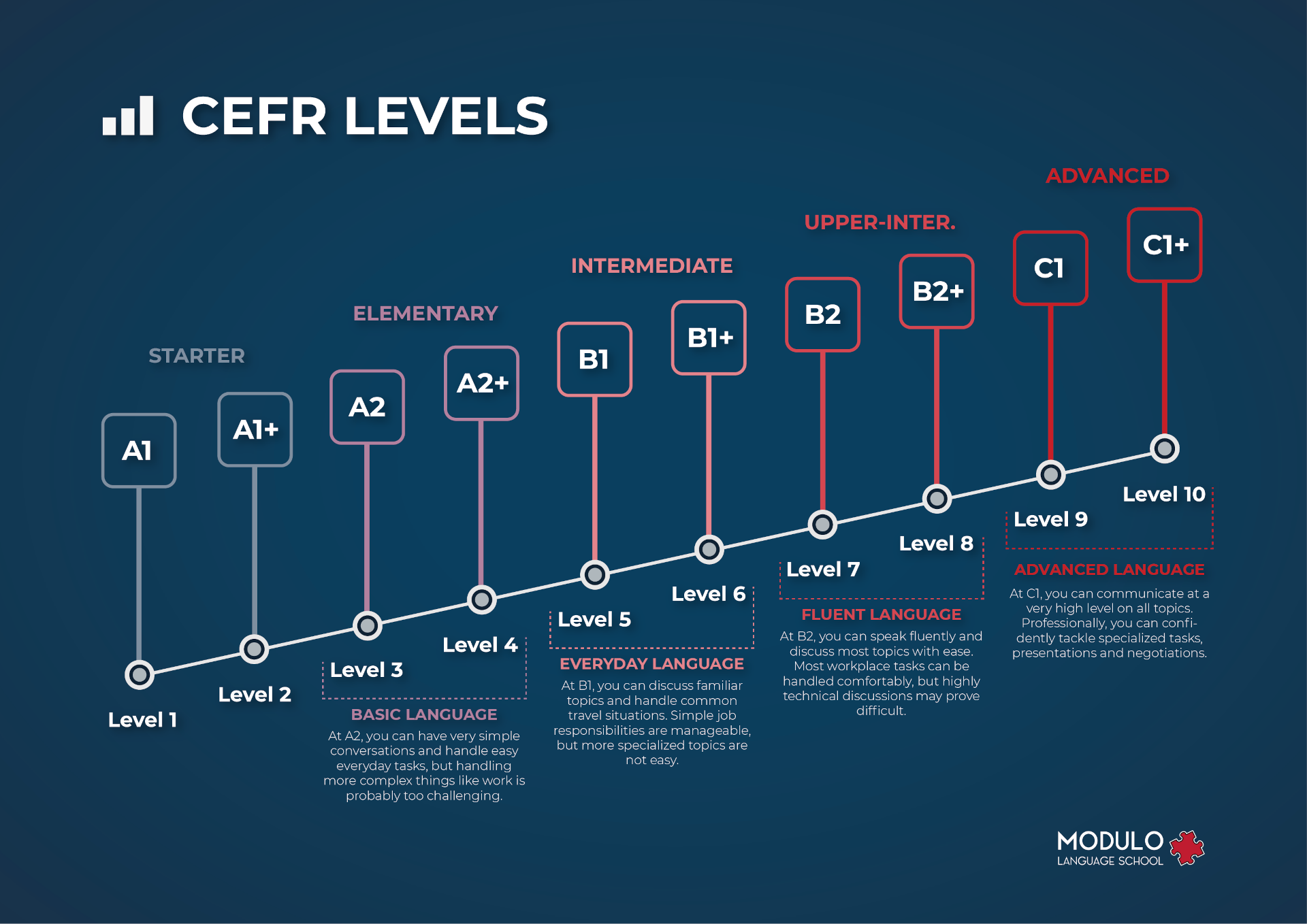
Based on 20 years of research, the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) was developed. This framework measures one’s level of language proficiency. It is divided into three level groups (Basic User, Independent User and Proficient User) and six levels (A1, A2, B1, B2, C1 & C2). Beginning learners and most children start with the most basic level, which is A1 (the breakthrough or beginner level).
A1 speakers can understand and use familiar everyday expressions and very basic phrases. Furthermore, they can also introduce themselves and others and can ask and answer questions about personal details such as where they live, people they know and things they have. Lastly, they can interact in a simple way provided the other person talks slowly and clearly and is prepared to help.
How Does One Reach A1?

One can reach the A1 level by learning basic expressions, basic vocabulary words and basic grammar.
Basic Expressions

They can start out with the most basic expressions, which will come in handy during introductions and casual conversations.
- Welcome!
- Hello!
- How are you?
- I’m fine!
- Long time no see!
- What’s your name?
- My name is… / I am…
- Where are you from?
- I am from… / I am…
- Nice/Pleased to meet you!
- Good morning!
- Good afternoon!
- Good evening!
- Good night!
- Goodbye!
- Good luck!
- Have a nice day!
- Bon appetit!
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
- Do you understand?
- I understand.
- I don’t understand
- Please speak more slowly.
- Please say that again.
- Please write that down.
- Do you speak…?
- Yes, a little.
- Please speak to me in…?
- How do you say…in…?
- Excuse me!
- How much is this?
- I’m sorry!
- Please
- Thank you!
- Where’s the toilet/bathroom?
- I love you!
- Holiday and Birthday Greetings
When learning these phrases and while learning a language, it is also good to learn about the formal and polite forms of the language. Certain languages, such as Japanese and Korean, use special verbs and verbs that can conjugate or change based on politeness and honorifics. Languages, such as French, Spanish, Italian, German, Bahasa Melayu/Indonesia and Mandarin Chinese, use a polite pronoun to refer to the addressee (“you”) (Vous, Usted, Lei, Sie, Anda & 您 nín). Others, such as Tagalog and Thai, use polite particles or words (po & ครับ krap / ค่ะ ka). Have your children or learners practice these expressions with simple dialogues and conversations. (Daniel: Hi, my name is Daniel. Kevyn: It’s nice to meet you, my name is Kevyn)
Basic Words to Learn

When you learn a language, you learn the basic words and lists of related words in the language. A group of language learners created a list of 625 essential words that can provide a foundation in one’s language learning. These words are grouped into different categories and can prove useful helping one learn words for conversations and basic stories and media. You can divide each lesson according to the different categories.
- Animal: dog, cat, fish, bird, cow, pig, mouse, horse, wing, animal
- Transportation: train, plane, car, truck, bicycle, bus, boat, ship, tire, gasoline, engine, (train) ticket, transportation
- Location: city, house, apartment, street/road, airport, train station, bridge, hotel, restaurant, farm, court, school, office, room, town, university, club, bar, park, camp, store/shop, theater, library, hospital, church, market, country (USA, France, etc.), building, ground, space (outer space), bank, location
- Clothing: hat, dress, suit, skirt, shirt, T-shirt, pants, shoes, pocket, coat, stain, clothing
- Color: red, green, blue (light/dark), yellow, brown, pink, orange, black, white, gray, color
- People: son, daughter, mother, father, parent (= mother/father), baby, man, woman, brother, sister, family, grandfather, grandmother, husband, wife, king, queen, president, neighbor, boy, girl, child (= boy/girl), adult (= man/woman), human (≠ animal), friend (Add a friend’s name), victim, player, fan, crowd, person
- Job: Teacher, student, lawyer, doctor, patient, waiter, secretary, priest, police, army, soldier, artist, author, manager, reporter, actor, job
- Society: religion, heaven, hell, death, medicine, money, dollar, bill, marriage, wedding, team, race (ethnicity), sex (gender), murder, prison, technology, energy, war, peace, attack, election, magazine, newspaper, poison, gun, sport, race (sport), exercise, ball, game, price, contract, drug, sign, science, God
- Art: band, song, instrument (musical), music, movie, art
- Beverages: coffee, tea, wine, beer, juice, water, milk, beverage
- Food: egg, cheese, bread, soup, cake, chicken, pork, beef, apple, banana, orange, lemon, corn, rice, oil, seed, knife, spoon, fork, plate, cup, breakfast, lunch, dinner, sugar, salt, bottle, food
- Home: table, chair, bed, dream, window, door, bedroom, kitchen, bathroom, pencil, pen, photograph, soap, book, page, key, paint, letter, note, wall, paper, floor, ceiling, roof, pool, lock, telephone, garden, yard, needle, bag, box, gift, card, ring, tool
- Electronics: clock, lamp, fan, cell phone, network, computer, program (computer), laptop, screen, camera, television, radio
- Body: head, neck, face, beard, hair, eye, mouth*, lip*, nose, tooth, ear, tear (drop), tongue, back, toe, finger, foot, hand, leg, arm, shoulder, heart, blood, brain, knee, sweat, disease, bone, voice, skin, body
- Nature: sea, ocean, river, mountain, rain, snow, tree, sun, moon, world, Earth, forest, sky, plant, wind, soil/earth, flower, valley, root, lake, star, grass, leaf, air, sand, beach, wave, fire, ice, island, hill, heat, nature
- Materials: glass, metal, plastic, wood, stone, diamond, clay, dust, gold, copper, silver, material
- Math/Measurements: meter, centimeter, kilogram, inch, foot, pound, half, circle, square, temperature, date, weight, edge, corner
- Miscellaneous Nouns: map, dot, consonant, vowel, light, sound, yes, no, piece, pain, injury, hole, image, pattern, noun, verb, adjective
- Directions: top, bottom, side, front, back, outside, inside, up, down, left, right, straight, north, south, east, west, direction
- Seasons: Summer, Spring, Winter, Fall, season
- Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 30, 31, 32, 40, 41, 42, 50, 51, 52, 60, 61, 62, 70, 71, 72, 80, 81, 82, 90, 91, 92, 100, 101, 102, 110, 111, 1000, 1001, 10000, 100000, million, billion, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, number
- Months: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December
- Days of the week: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday
- Time: year, month, week, day, hour, minute, second , morning, afternoon, evening, night, time
- VERBS: work, play, walk, run, drive, fly, swim, goC, stop, follow, think, speak/say, eat, drink, kill, die, smile, laugh, cry, buy*, pay*, sell*, shoot(a gun), learn, jump, smell, hear* (a sound), listen* (music), taste, touch, see (a bird), watch (TV), kiss, burn, melt, dig, explode, sit, stand, love, pass by, cut, fight, lie down, dance, sleep, wake up, sing, count, marry, pray, win, lose, mix/stir, bend, wash, cook, open, close, write, call, turn, build, teach, grow, draw, feed, catch, throw, clean, find, fall, push, pull, carry, break, wear, hang, shake, sign, beat, lift
- ADJECTIVES: long, short (long), tall, short (vs tall), wide, narrow, big/large, small/little, slow, fast, hot, cold, warm, cool, new, old (new), young, old (young), good, bad, wet, dry, sick, healthy, loud, quiet, happy, sad, beautiful, ugly, deaf, blind, nice, mean, rich, poor, thick, thin, expensive, cheap, flat, curved, male, female, tight, loose, high, low, soft, hard, deep, shallow, clean, dirty, strong, weak, dead, alive, heavy, light (heavy), dark, light (dark), nuclear, famous
- PRONOUNS: I, you (singular), he, she, it, we, you (plural, as in “y’all”), they.
Basic Grammar

In a language, it is important to learn grammar. Grammar will allow learners to create proper sentences to express themselves. In this part, basic and useful grammar structures will be discussed. These will help your child and learners express simple things well.
- Word Order (Subject-Verb-Object, Subject-Object-Verb, Verb-Subject-Object, etc.)
- To be (Dave is a teacher; Dave est un professeur)
- Some languages may not have the “to be” verb (Dave guru; Guro si Dave)
- Some languages have various ways to conjugate/change the verb “to be” (I am – yo soy; You are – tu eres; She is – ella es; We are –nosotros somos; Y’all are – vosotros sois; They are – ellos son)
- Questions (Is Dave a teacher?; Dave est-il un professeur?)
- Some languages use question particles (Is Dave a teacher? デイヴは先生ですか? Dave-wa sensei desu ka?)
- Negatives (Dave is not a teacher; Dave n’est pas un professeur?)
- Possession (The teacher‘s book; 先生の本 Sensei-no hon)
- Possessive Pronouns (My book; Mein Buch)
- Some languages use suffixes to indicate the possession of a pronoun (My book; كتابي kitab-i; ספרי sifr-i)
- Demonstratives (this, that, here, there; itó, iyán, iyón, díto, diyán, doón)
- Question Words (what, when, where, who, which, why, and how; was, wann, wo, wer, welche, warum, wie)
- Simple Present (The student goes to school; Lo studente va a scuola)
- Prepositions (The girl went to the room; A menina foi para o quarto)
- Some languages use postpositions (Above the table; 식탁 위에 Shikthak ui-e)
- Some languages use noun case suffixes (Inside the house; Talossa)
- Would like (I would like a cup of tea, please; Me gustaria una taza de té, por favor)
- Frequency Adverbs (I often eat curry; 저는 자주 카레를 먹습니다 Chŏ-nŭn chaju khare-rŭl mŏksŭmnida)
- Time (I will go tomorrow; 我明天会去; Wǒ míngtiān huì qù)
- There is/are (There is a toilet there; Ada kamar kecil di sana)
- To have (I have a pencil; 저는 연필이 있어요 Chŏ-nŭn yŏnpir-i issŏyo)
- Conjunctions (and, or…; y, o…)
- Simple Past (The boy ate fish yesterday; A fiú tegnap halat evett)
- Some languages do not have tenses (The boy “eats” fish yesterday; เด็กชายกินปลาเมื่อวานนี้ Dèk-chhaai kin plaa mʉ̂ʉa-waan-níi)
- Also, Too (Hanna is also Korean; 한나도 한국 사람이에요 Hanna-do Hanguk saram-ieyo)
- Adjectives (The boy is tall; Мальчик высокий Mal’chik vysokiy)
- In some languages, adjectives can act as verbs (The car was red OR The will-be-red car; 차는 빨갰어요 Chha-nŭn ppalgæssŏyo OR 빨갈 차 ppalgal ccha)
- In some languages, the verb has to agree with the declension/changes of the noun (The old building; Staremu budynkowi)
- Progressive Tense (I am going to school now; Estoy yendo a escuela ahora)
- Some languages do not have progressive tenses though (I go to school now; Ich gehe zur Schule jetzt)
- Imperatives or Command Words (Please write; 書いて下さい Kaite kudasai)
- May, Can, Might, Could, Would, Have to, etc. (He can read Japanese; 彼は日本語が読めます; Kare-wa Nihongo-ga yomemasu)
- Comparatives and Superlatives more, -er, most, -est (He is faster than me; 他比我快 Tā bǐ wǒ kuài)
- To go / To come + verb (I will come home to eat; 私は食べに帰ります Watashi-wa tabe-ni kaerimasu)
- Indirect Quotations said, thought, heard (I heard that Yuri came back; 저는 유리가 돌아온다고 들었어요 Chŏ-nŭn Yuri-ga tora-ondago tŭrŏssŏyo)
- like + -ing / to… ( I like traveling; Ich reise gerne)

Here in AHEAD, we have various services and tutors that can help your child and learner learn more. We believe in giving you the best and opportunities through language learning. Stay tuned for more language-learning articles.
